INTRODUCTION
Owing to the rapid rise in the worldwide demand for poultry meat, the efficient production of poultry meat has been an important issue [1]. Quantitative traits such as growth rate and carcass percentage are important economic traits and critical factors to increase poultry meat production [2]. Traditionally, these traits were improved by breeding and feeding [3,4], however, their molecular mechanisms were not clear. Recently, numerous genetic and functional studies are being conducted to understand the skeletal muscle development [5,6]. This information could provide insights to improve the efficiency of poultry meat production.
Muscle is an essential tissue that helps with movement and support of the body. It is composed of bundles of multinucleated fusion cells called myofibers. Myogenesis occurs through myoblast fusion, which is initiated and regulated by various transcription factors and mechanisms. Generally, myogenesis is controlled by regulatory factors called paired box (PAX) genes and myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) [7]. The PAX genes act as regulators of myoblast or satellite cell proliferation and differentiation during early myogenesis [8]. MRFs are composed of four genes (myogenic differentiation 1 [MYOD1], myogenic factor 5 [MYF5], myogenin [MYOG], and myogenic factor 6 [MYF6]), which play major regulators of muscle differentiation. They can even induce myogenic differentiation in non-myogenic cells [9–11]. Myostatin (MSTN), which belongs to the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily, plays an important role as a negative regulator of skeletal muscle growth in animals [12]. It is mainly expressed in skeletal muscles [13]. Previous studies have reported that various species with naturally occurring mutations in MSTN, as well as species with MSTN knockout models, have demonstrated increased skeletal muscle mass [14–17]. Keller-Pinter et al. demonstrated that Syndecan-4 (SDC4) affects myoblast proliferation by modulating MSTN signaling [18]. Research regarding the relationship between MSTN and myogenesis has resulted in the emergence of myoblasts as an important factor related to the development of the poultry industry.
SDC4 is a heparan sulfate proteoglycan, composed of a core protein connected to glycosaminoglycan chains, which are one or more long linear carbohydrate chains [19]. It belongs to the syndecan family that regulates integrin by interacting with fibronectin and signaling proteins found in the basement membrane [20]. Like SDC2, SDC4 has glycosaminoglycan chain that attaches to heparan sulfate [18]. Despite being the smallest protein in the syndecan family, SDC4 has been studied the most. While its molecular mechanisms have not been sufficiently established, SDC4 is known to affect muscle differentiation and production [19]. Its important role in muscle development, maintenance, and regeneration is being investigated in mice, turkeys, and bovines. More myotubes are formed when the SDC4 gene is knocked out in bovine muscle cells. Moreover, other studies have shown that SDC4 knockout causes muscle damage by reducing the number of satellite cells in case of disease in mice and turkeys [21–23]. These results may support that SDC4 has an effect of inhibiting muscle development. And this inhibitory effect could be mediated by various genes and factors that negatively affect for the differentiation, such as MSTN and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) [18,22]. Therefore, the expression of SDC4 must be decreased during normal muscle differentiation.
Although previous studies have actively investigated the role of SDC4 in satellite cells [21,23–25], research regarding its involvement in muscle differentiation is still limited. This study hypothesized that SDC4 plays a crucial role in muscle growth and development particularly through regulating MRFs. To reveal its effects on quail muscles, either SDC4 expression vector or an empty vector (EV) was transfected into quail myoblasts (QM7) cells, and the differentiation of the cells was compared by analyzing myotube formation. Subsequently, changes in the expression of MRFs and MSTN in the cells overexpressing SDC4 were analyzed and compared with those factors in the control cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The effect of SDC4 on muscle differentiation was investigated by performing a series of experiments with three replicates. Each replicate consisted of two groups: SDC4-overexpressed (OE) and control. QM7 cells from different passages were used for each replicate. Each of the 14 Ф35-mm dishes was seeded with 8 × 105 cells 1.5 d before starting differentiation (day 0). On the day before differentiation, the cells were transfected with either SDC4-expression vector or EV. Differentiation was observed at four time points: day 0, the start of differentiation; day 1, the change of myogenic gene expression; day 2, the active myotube formation; and day 4, the sufficient myotube formation. mRNA samples were collected at four time points (day 0, 1, 2, 4), protein samples at two time points (day 0, 4), and immunofluorescence samples at one time point (day 4). Each sample was prepared at each time point for further analysis.
The coding sequence of SDC4 was amplified with a primer set, SDC4-f (5’-GTT CCG TTC TGA TTC AGC GC-3’) and SDC4-r (5’-CTC ATT GGA GGG CAC AGT GT-3’), by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and cloned into the pGEM-T easy vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). After confirming the sequence of the SDC4 gene by Sanger sequencing, the hemagglutinin (HA)-tag sequence was added in front of the stop codon of the SDC4 gene by PCR with a primer set, SDC4-f and SDC4-HA-r (5’-TTA CAA GCT GTA ATC TGG ACC ATC GTA TGG GTA AGC ATA GAA CTC ATT TGT AGG-3’). Then, the amplified sequence was inserted into the EcoRV site of the pcDNA3.1 vector (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY, USA) to generate the final SDC4 expression vector.
QM7 cells (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) were cultured in medium 199 containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA), 10% tryptose phosphate broth (TPB; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (ABAM; Gibco). The cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 and subcultured before filling in the culture dish to prevent differentiation. To promote cell differentiation, the differentiation medium was prepared by changing the FBS concentration to 0.5%; all remaining compositions and conditions were the same. The cells were seeded at density of 8 × 105 in a culture dish and transfected with EV or SDC4 expression vector after 18 h using Lipofectamine 3000 reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. For the control, the pcDNA3.1 designated as EV was used. The culture medium was replaced with fresh growth medium at 5 h after transfection. After 16 h, the culture medium was replaced with the differentiation medium. They were differentiated for 4 d, and from day 2, half the culture medium was replaced with fresh differentiation medium every day.
The cells were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed for 15 min using 10% neutral-buffered formalin. Cell membrane permeability was induced using 0.3% NP-40. The non-specific antigens were blocked using PBS mixed with 0.1% Tween-20 (PBST) containing 5% non-fat dry milk. The primary antibody was treated with anti-myosin heavy chain (MF20; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA, USA) for 1 h and the secondary antibody with anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA) conjugated with CruzFluorTM594. The nuclei were then stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Photographs were captured using an inverted fluorescent microscope (CKX53; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). To measure the area of differentiated myotubes, the photographs of immunofluorescence-stained cells were used to measure the length and thickness of myotubes.
The cells were washed with PBS and extracted in 1× lysis buffer. Cellular debris was removed by centrifuging at 14,000×g for 10 min at 4°C. Subsequently, the same amount of 2 × Laemmli buffer, containing 2-mercaptoethanol, as that of the supernatant, excluding the pellets, was added. The protein was denatured at 95°C for 5 min. Protein concentrations were measured using Coomassie staining, and they were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The protein samples were transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Subsequently, the non-specific antigens were blocked using 5% non-fat dry milk in Tris-buffered saline mixed with Tween-20 (TBST). After processing the primary antibodies overnight at 4°C, the secondary antibodies were processed at room temperature. During treatment with antibodies, the concentration of skim milk was lowered to 2.5%. After processing the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) solution, images were obtained using the ImageQuant LAS 500 imager (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA).
When the cultured cells reached a density of 8 × 105 QM7 cells in the culture dish, they were differentiated after 42 h to ensure sufficient growth. The differentiated mRNA samples were extracted on days 0, 1, 2, and 4 using RNAiso plus (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). Total RNA was identified and 1 μg was quantified using the P200 Micro-volume spectrophotometer (Biosis Design, Gwangmyeong, Korea) and by electrophoresis. cDNA was prepared using the DiaStarTM RT Kit (SolGent, Daejeon, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, cDNA was subjected to qRT-PCR using the Bio Rad CFX Connect™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Target genes were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) that was used as the housekeeping gene. Table 1 shows the primer pairs designed for qRT-PCR. The expression level of the target gene was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method.
All data were expressed as the mean ± SEM and analyzed using Student’s t-test and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in R packages (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Multiple groups showing significance in the groups were compared using the least significant difference (LSD) test. The results were considered significant if p < 0.05. All experiments were independently conducted in triplicate.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
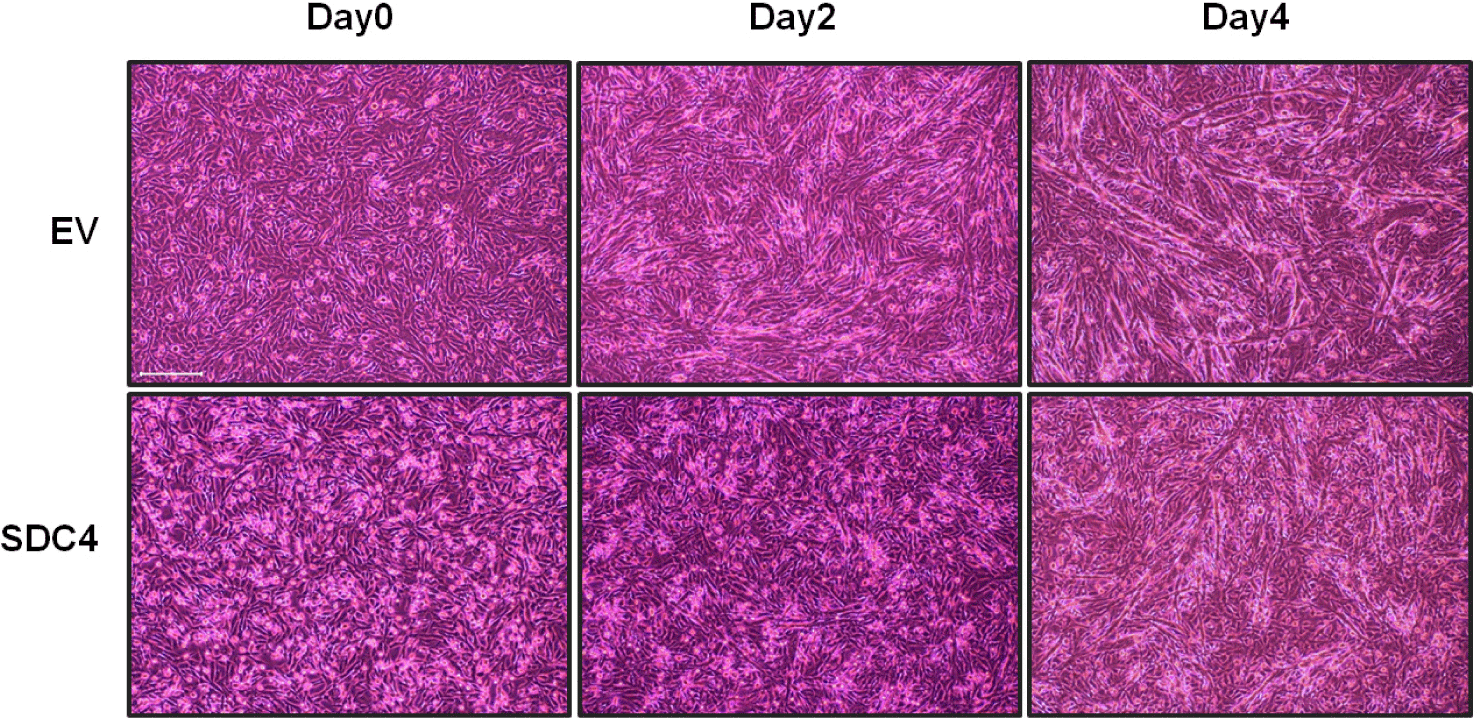
An overexpression vector of SDC4 was designed and transfected into QM7 to verify the effect of SDC4 on muscle cell differentiation. SDC4-OE cells showed lesser muscle cell differentiation than did the EV cells, which were used as the control cells (Fig. 1). Differentiation was observed at four time points: day 0, the start of differentiation; day 1, the change of myogenic gene expression; day 2, the active myotube formation; and day 4, the sufficient myotube formation. Distinctive differences in myotube formation were observed during days 2–4 after differentiation between the groups. On day 2, while the EV cells started forming myotubes, the SDC4-OE cells did not. Myotube formation in SDC4-OE cells was observed on day 4, and its rate was as low as that observed in the EV cells on day 2. The myotubes in the SDC4-OE cells were shorter and thinner than those in the EV cells on day 4. Therefore, SDC4 is a negative regulator of myotube formation.
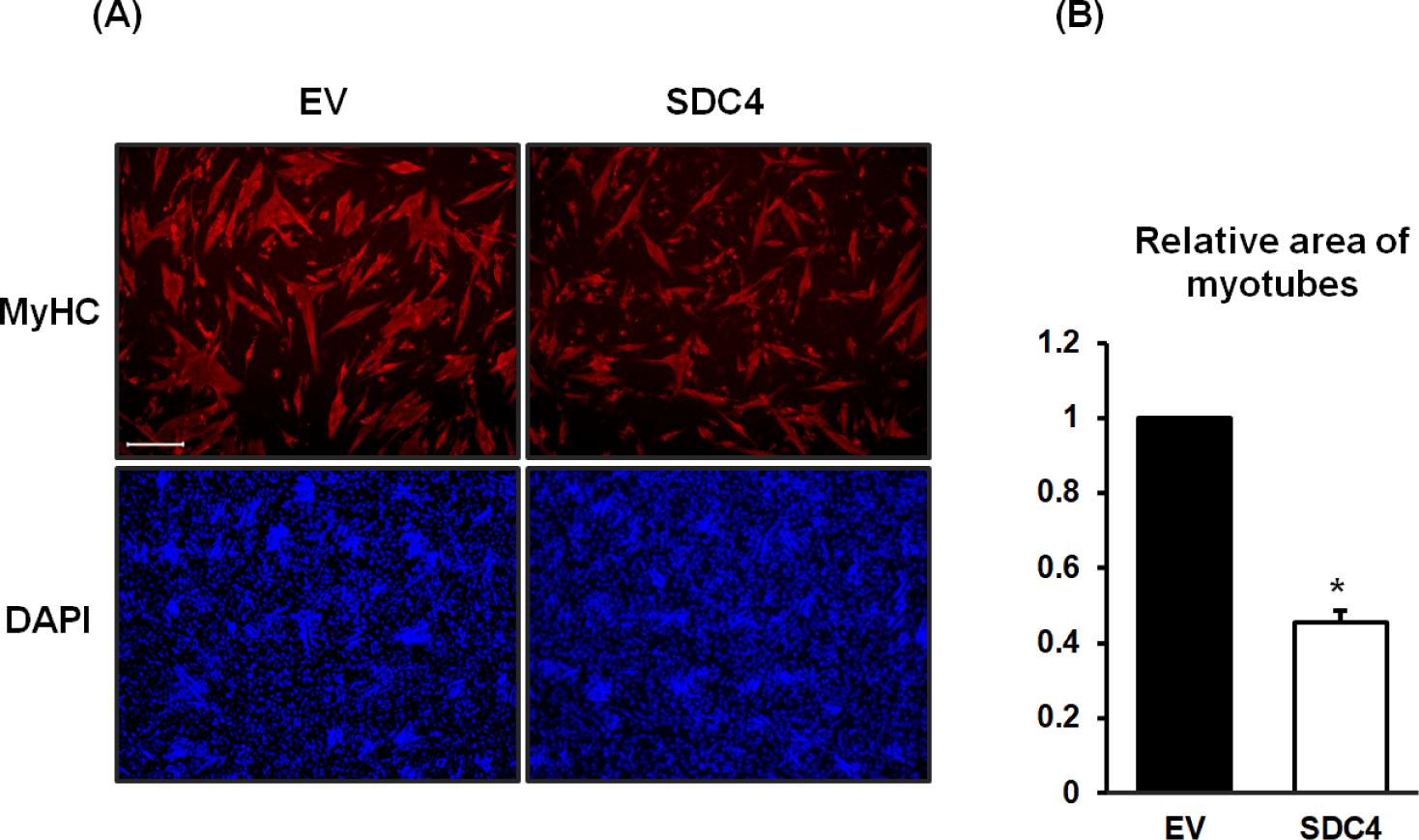
To observe and measure the relative area of the myotubes, they were stained with anti-myosin heavy chain (MyHC) antibodies and DAPI on day 4 (Fig. 2). As shown in Fig. 1, the myotubes of the SDC4-OE cells were narrower and shorter than those in the control cells (Fig. 2A). Among the stained cells, the number of mononucleated cells was higher in the SDC4-OE cells than that of those in the control cells, suggesting that fusion of the myocytes is inhibited by SDC4. The myotube area of SDC4-OE cells was reduced by less than half of that of the control cells (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2B).
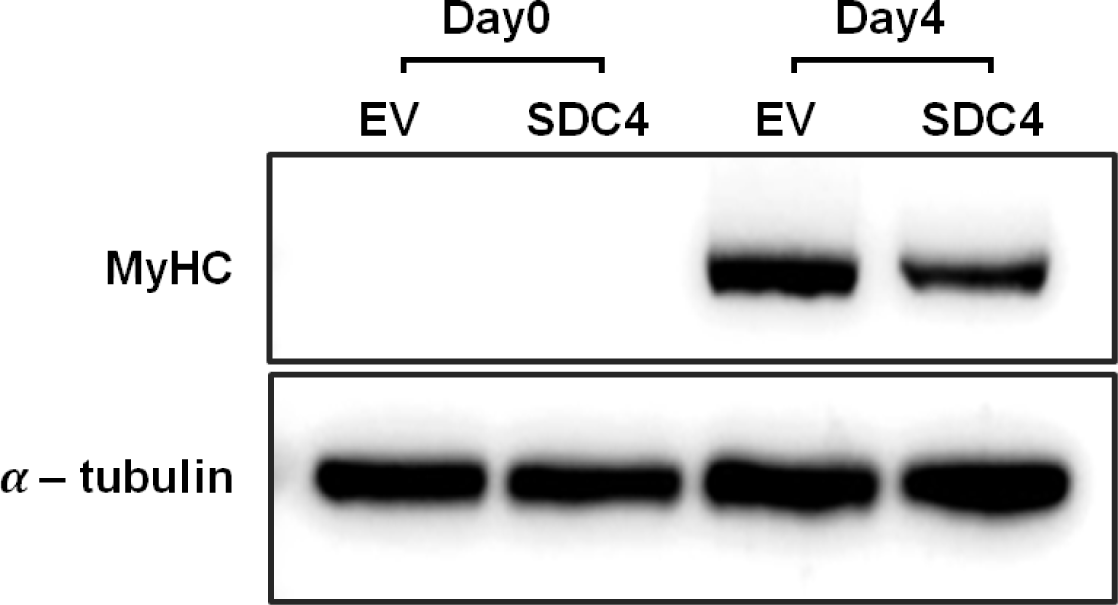
To confirm the degree of differentiation between the groups at a molecular level, western blotting was performed using MyHC, which is the most abundant protein responsible for muscle contraction in the skeletal muscles [26]. MyHC protein was not observed on day 0 in both groups, suggesting that the cells had not started differentiating at that time (Fig. 3). However, MyHC protein was detected on day 4 at different levels in both groups. The amount of MyHC protein in the SDC4-OE cells was less than half of that in the control cells. Myotube staining showed similar results, indicating that myotube formation was reduced by SDC4 overexpression. Similarly, a previous study showed that myotube formation, which is increased by SDC4 knockout in bovine cells and the cytoplasmic domain of SDC4, inhibits myoblast fusion [22]. Szabo et al. reported that SDC4 expression gradually decreases during muscle differentiation, while high expression of SDC4 hinders myogenesis [27]. Decreasing SDC4 expression during myogenesis is crucial for myotube formation. In summary, SDC4 plays a role in inhibiting myocyte fusion and myotube formation, which leads to reduced myogenesis.
The effect of SDC4 on the expression of genes known to regulate myotube formation was investigated via qRT-PCR (Fig. 4). PAX3 and PAX7, which are expressed in the early stages of muscle development and are involved in the proliferation of myoblasts and initiation of myogenic differentiation [28], showed no differences between the groups. However, they were significantly reduced during differentiation (p < 0.01) (Figs. 4A and 4B), indicating that SDC4 does not affect the initiation of differentiation by regulating PAX3 and PAX7 expression.
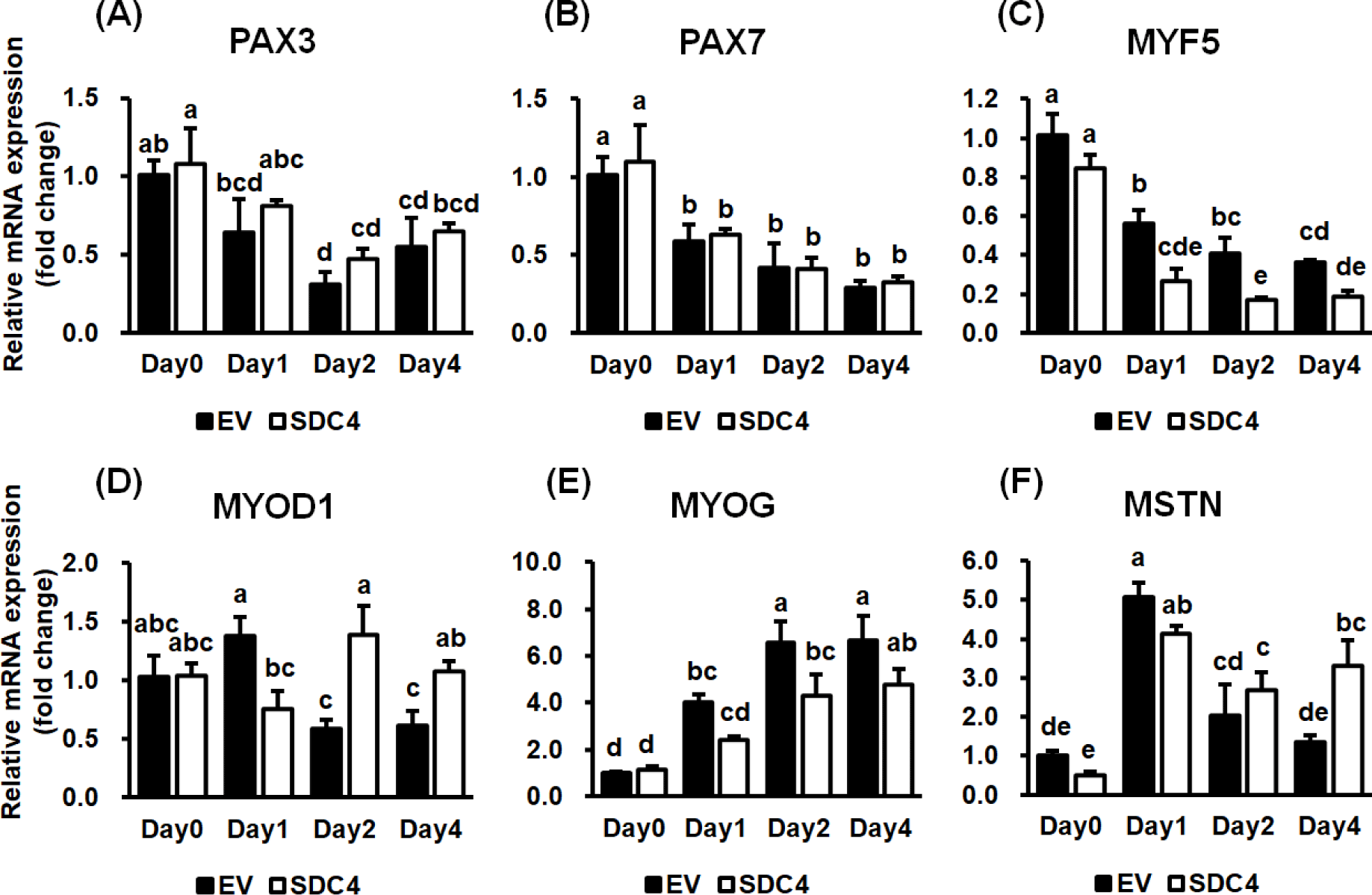
Subsequently, the expression of MRFs was analyzed. MYF5 showed a continuous, significant reduction in expression during differentiation in both groups (p < 0.001) (Fig. 4C). MYF5 expression was significantly lesser in the SDC4-OE cells than in the control cells on days 1 and 2 (p < 0.001). Among the MRFs, MYF5 is expressed first and initiates differentiation of muscle progenitor cells into myoblasts. It is turned off when MYOD1 is expressed in the myoblasts [29]. These results suggest that decreased expression of MYF5 by SDC4 cannot adequately induce differentiation of progenitor cells and may lead to insufficient expression of MYOD1.
The expression of MYOD1 was significantly affected by the interaction between the day of differentiation and treatment (p < 0.01) (Fig. 4D). The expression level of MYOD1 was the same between the groups before differentiation but differed significantly after initiation of differentiation. In the control group, the expression of MYOD1 increased on day 1 and then decreased from day 2 onward. In SDC4-OE cells, MYOD1 expression decreased slightly on day 1 and increased from day 2. MYOD1 expression in the control group was significantly higher than that in the SDC4-OE cells on day 1, whereas it was significantly higher in the SDC4-OE cells from day 2. MYOD1 expression is known to increase in highly proliferative myoblasts; it then decreases after inducing the expression of MYOG to initiate myotube formation [30,31]. In this study, SDC4 altered the expression of MYOD1 in a different pattern, maintaining higher expression in the mid and late stages of differentiation, which resulted in delayed myoblast differentiation and myotube formation.
MYOG expression gradually increased during myogenesis in both groups (p < 0.001); however, its expression in the SDC4-OE cells was lower than that in the control cells during differentiation (p < 0.01) (Fig. 4E). Increased MYOG expression is known to enhance myotube formation during differentiation. During differentiation, MYOG is upregulated to induce differentiation of myoblasts into myotubes, which is accompanied by the downregulation of MYOD1 [32,33]. Sustained expression of MYOD1 during differentiation may aid in proliferation of the myoblasts rather than differentiation in SDC4-OE cells. Additionally, the previous study reported that a defect in MYOG results in a severe reduction of all skeletal muscles [34]. In this study, the lower expression of MYOG due to SDC4 overexpression may also delay myoblast differentiation. SDC4 plays a role in recruiting FGF to transmit signals across the cell membrane and acts as a co-receptor for FGF receptor (FGFR). FGF2 is known to reduce the expression of MYOG, thus acting as an inhibitor of skeletal muscle differentiation [35]. Hence, decreased MYOG expression and myotube formation may be caused by elevated FGF2 signaling owing to SDC4 overexpression.
Expression pattern analysis of the MSTN gene, which does not belong to the MRF family but is closely related to the regulation of muscle development, was conducted [36]. A significant change in MSTN expression was observed in both groups depending on the day of differentiation but not on treatment (p < 0.001) (Fig. 4F). MSTN expression increased dramatically on day 1 and then decreased sharply in the control cells but not in the SDC4-OE cells. The interaction between the day of differentiation and treatment had a significant effect on MSTN expression (p < 0.05); it was higher in the SDC4-OE cells on day 4. SDC4 was recently reported to reduce the formation of mature MSTN by binding to proMSTN [18], which usually gets reduced because of conversion into mature MSTN through a proteolytic process. However, SDC4 blocks this process, thus reducing the amount of mature MSTN, which induces the proliferation of myoblasts during the early stage of skeletal muscle regeneration. In this study, the higher level of MSTN expression maintained during differentiation in SDC4-OE cells might have inhibited myoblast proliferation and differentiation. The inhibitory effect of MSTN may get gradually elevated because of reduced transiently expressed SDC4 during differentiation.
SDC4 is highly expressed during satellite cell proliferation in turkeys [37]. In an SDC4-knockout mouse model, muscle recovery abilities were distinguishably decreased, and the muscle fibers were smaller than those in the control group [38]. Moreover, the model exhibited defects in satellite cell activation, proliferation, and MYOD1 expression [23]. These studies showed that SDC4 is closely associated with regeneration through activation and proliferation of satellite cells. This finding along with our data shows that an appropriate level of SDC4 is required for normal proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts during muscle development. MSTN is also known to inhibit myoblast differentiation by reducing MYOD1 synthesis and activity [39]. In this study, both MSTN and MYOD1 were upregulated in SDC4-OE cells on day 4. These results suggest that there could be another pathway, including SDC4 signaling cascades, affecting MSTN and MYOD1 regulation.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the effect of SDC4 on muscle cell differentiation and elucidates various changes in gene expression. In quail muscle cells, SDC4 reduces myotube formation and negatively affects muscle formation. This inhibitory effect of SDC4 on muscle formation is mediated by regulation of the expression of MRFs and MSTN. This finding may help to elucidate the intricate molecular mechanisms of SDC4 and to comprehend muscle development, disease, and regeneration. Furthermore, it could enhance poultry production, which would be advantageous for poultry breeders. However, further studies are necessary to unveil the intricate mechanisms underlying the modulation of the expression of MRFs and MSTN by SDC4.
















